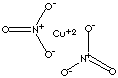| COPPER NITRATE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 3251-23-8
(n-hydrate) 10031-43-3 (Trihydrate) 19004-19-4 (hemipentahydrate) |
|
|
EINECS NO. |
221-838-5 | |
| FORMULA | Cu(NO3)2 | |
| MOL WT. | 187.56 | |
|
H.S.CODE |
||
| TOXICITY | Oral rat LD50: 940 mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | Copper Dinitrate; Cupric Nitrate; | |
| cupric nitrate, n-hydrate; Nitric Acid, Copper (2+) salt; Kupferdinitrat (German); Dinitrato de cobre (Spanish); Dinitrate de cuivre (French); | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES (TRIHYDRATE) |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | dark blue crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | 114 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 2.05 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | 8.33 | |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0; Special Hazard: OX | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | Not considered to be a fire hazard | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF COPPER COMPOUNDS & APPLICATIONS | ||
Copper forms compounds in the oxidation states of +1 (cuprous) and +2 (cupric);
trivalent copper survives no more than a few seconds in an aqueous solution. The
relatively small change in electrochemical potential between the cuprous and
cupric ions in solution gives the usefulness of copper compounds in chemical
reactions. Copper compounds are used as catalysts in reactions, especially
oxidation (cupric chloride) and heterogeneous reactions. Cupric chloride, copper
chloride (CuCl2) is a yellowish to brown, deliquescent powder; soluble in water,
alcohol, and ammonium chloride; while the dihydrated form of cupric chloride is
a green crystals; soluble in water. It is used as a mordant in dyeing and
printing textile fabrics and in the refining of copper, gold, and silver as well
as a catalyst in chemical reactions. Cuprous chloride (CuCl or Cu2Cl2), also
known as resin of copper, is a green, tetrahedral crystals; insoluble in water.
The biological property of copper compounds takes important role in as
fungicides in agriculture and biocides in antifouling paints for ships and wood
preservations. Very low level of copper is toxic to fungi and algae but the
levels for mammal is much higher. The copper ions inhibit the metabolism of the
fungus when they react with sulfur containing enzymes in the plant. Copper
compounds form a protective barrier on the plant surface and thereby prevent
fungi from entering the plant host. The fungicidal effect of copper compounds as
non-systemic fungicides are such as bordeaux mixture, cupric hydroxide, copper
arsenate, copper carbonate, cuprous oxide, copper-8-quinolinolate, copper
oleate, copper sulfate, or copper oxychloride. Another important biological
application of copper compounds, such as copper sulfide is as an antifouling agent
in paints. The description and applications of copper compounds in
industry are;
Copper sulfate is the common name for the blue crystalline cupric sulfate, in which copper has valence +2. It may also refer to cuprous sulfate (Cu2SO4), in which copper has valence +1. It is soluble in water but insoluble in alcohol. It usually crystallizes as a pentahydrate compound containing five molecules of water (CuSO4·5H2O) and is known in commerce as blue vitriol. It is prepared by the treatment of copper oxides with sulfuric acid. Cupric sulfate is the most important salt of copper. Cupric sulfate is utilized chiefly for agricultural purposes, as a pesticide, germicide, feed additive, and soil additive. It is also used as a raw material in the preparation of other copper compounds, electrolyte for batteries and electroplating baths, and in medicine as a locally applied fungicide, bactericide, and astringent. It also finds wide use in the preparation of pigments. Copper is an essential trace nutrient which performs a number of diverse functions in protein biochemistry. Some copper compounds such as copper sulfate are used as a supplement for livestock. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
dark blue crystals | |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
| Cu | 27.0 % min | |
| ACID INSOLUBLES | 0.02% max | |
| SULFATE | 0.05% max | |
| Fe | 0.1% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kg in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 5.1 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. |
1477 |
|
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 36/38,
Safety Phrases: 26
|
||